Your pet’s skin and coat tell a great deal about their overall health and well-being and can acquire a multitude of conditions that cause itchy, flaky, or bumpy skin. Understanding these conditions is crucial, not only for providing the best care for your pet but also for keeping them comfortable. From pesky fleas to mysterious lumps, discover what common skin conditions may afflict your four-legged friend.
1: Allergies in pets
Allergies are one of the most prevalent pet skin conditions and can be caused by environmental allergens, fleas, food, fabrics, medications, and more. Overall, pets are most likely to be allergic to pollen, mold, dust mites, and flea bites, but they can develop a true allergic response to anything they encounter.
Pets with allergies often suffer from intense itching, hair loss, scabs, hot spots, chronic ear infections, or yeast or bacterial skin infections. An accurate allergy diagnosis may involve skin testing, blood tests, or dietary trials, and treatment options range from anti-itch medications and immunotherapy to flea preventives and prescription diets.
2: Lumps and bumps in pets
Skin lumps and bumps can arise from various causes and may range from harmless growths to potentially malignant tumors. Lumps can be raised bumps or nodules on the skin’s surface that vary in size, shape, and texture. Common causes include cysts, lipomas (i.e., benign fatty tumors), histiocytomas, mast cell tumors, and melanomas.
While some masses may be benign and pose no immediate threat to the pet’s health, others may require prompt veterinary attention for evaluation, diagnosis, and possible treatment. Monitor any new or changing lumps closely and seek veterinary advice if you see rapid growth, ulceration, or other concerning changes.
3: Ringworm in pets
Despite its name, ringworm is not caused by worms, but by a highly contagious fungus that infects the skin, hair, and nails. Ringworm lesions typically appear as circular, red, scaly patches with hair loss in the center. Treatment involves antifungal medications, medicated shampoos, and environmental decontamination.
4: Yeast and bacterial infections in pets
Yeast and bacterial skin infections often occur secondary to other skin conditions like allergies, trauma, hormonal imbalances, or excessive skin folds. Signs that may indicate your pet has a skin infection include redness, itching, greasy skin, pustules, crusty lesions, or a foul odor. Treatment often involves topical or oral antibiotics or antifungals, along with proper hygiene and addressing the underlying cause.
5: Hot spots on pets
Hot spots are localized areas of inflamed, infected skin that result from excessive licking, scratching, or moisture. They can seemingly pop up overnight and can worsen rapidly if left untreated. Treatment involves clipping hair around the affected area, cleansing with antiseptic solutions, topical or oral medications, and preventing further trauma through an Elizabethan collar.
6: Seborrhea in pets
Seborrhea is a skin disorder characterized by excessive sebum production or scaliness that can be inherited or secondary to other underlying conditions like allergies, hormonal imbalances, or parasites. Signs include greasy or flaky skin, odor, and hair loss, and treatment may involve medicated shampoos, dietary supplements, and addressing any underlying causes.
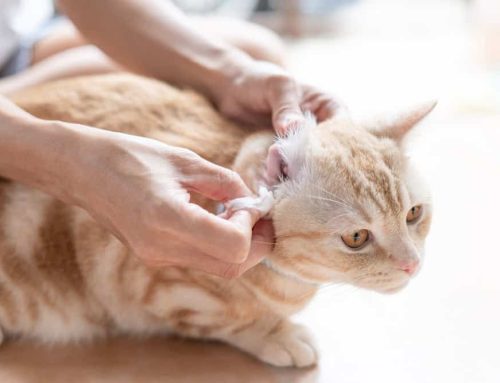
7: Ear mites in pets
Ear mites are tiny parasites that infest the ear canals, causing intense itching, inflammation, and dark discharge. Pets may frequently shake their heads or scratch their ears and can transmit ear mites to other pets. Treatment includes topical antiparasitic medications, along with thoroughly cleaning the ears.
8: Folliculitis and furunculosis in pets
Folliculitis pertains to hair follicle inflammation, while furunculosis is the formation of deep, painful skin abscesses. These conditions can be caused by bacterial or fungal infections, parasites, or trauma. Signs include redness, pustules, and nodules, while treatment involves antibiotics, antifungal medications, or surgical drainage of abscesses.
9: Anal gland issues in pets
The anal glands are small sacs located near the anus that secrete a foul-smelling substance. When these glands become impacted or infected, pets show their discomfort by scooting on the ground or licking excessively. Treatment involves manual gland expression, dietary fiber supplements to promote regular bowel movements, antibiotics if infection is present, and management of the underlying condition, such as allergies.
10: Mange in pets
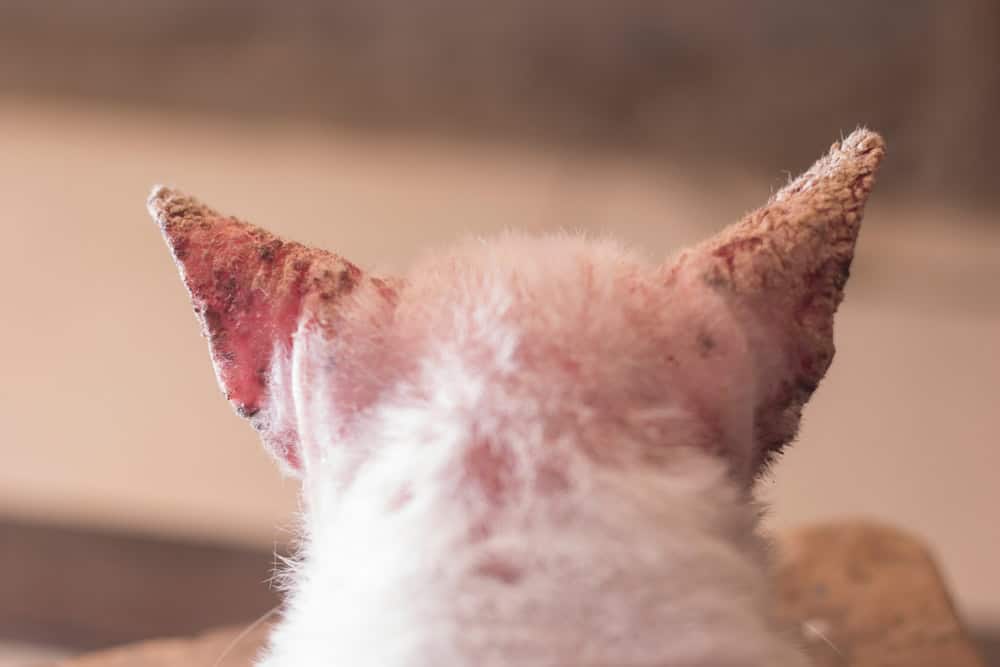

Mange is caused by mites that infest pets’ skin and hair follicles. Demodectic mange, which often affects young or immunocompromised animals, results when Demodex mites multiply rapidly because of immune system weakness. Sarcoptic mange, which is caused by highly contagious Sarcoptes mites, leads to intense itching and inflammation and spreads easily between pets and people.
Signs include patchy hair loss, red, inflamed skin, and secondary bacterial infections. Treatment involves medicated shampoos, topical and oral medications, and environmental decontamination to prevent reinfestation.
While some skin conditions will require professional diagnosis and treatment, good hygiene, preventive measures, and prompt veterinary care for any concerning issues are essential steps in safeguarding your pet’s skin health. Give our Kauai Veterinary Clinic team a call to schedule an appointment.









Leave A Comment